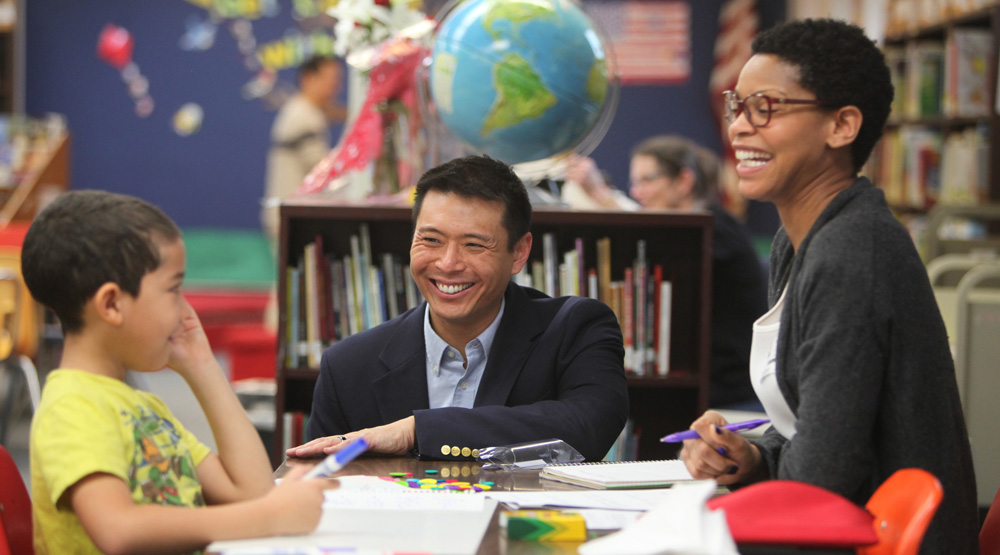

Prep schools, secondary schools that prepare students in preparation for higher education, are called prep schools. They can be public, private, or parochial schools. Prep schools are designed to prepare students for a successful future. While the specific curriculum of prep schools may vary, there are some common traits. These common characteristics include small class sizes, independent learning environments, music and fine arts programs.
Small class sizes
Smaller classes have many benefits for children. These benefits include higher test scores and student engagement as well as increased academic and life success. Also, smaller classes can have an impact on socioeconomic variables like lower crime and welfare dependence. In addition, students in smaller classes are more likely to attend college. This is particularly true for students from low-income and underrepresented communities.
Teachers can give students more personal attention if they have a smaller class size. Teachers are able to address individual needs and questions, and smaller classes give them more time to read student assignments. This gives students more personalized attention, which is essential for learning.

Music and fine arts programs
Prep schools often offer music and fine art programs that foster relationships between students. Many also offer many opportunities for students learning and performing. Students may choose from beginning, intermediate and advanced classes depending on what school they are attending. While entry-level courses are designed to teach students basic theory, techniques, intermediate and advanced classes will help them improve their artistic as well as analytical skills.
Schools offer education that is not only focused on the craft but also rigorous academics. Baltimore School for the Arts is one example. It teaches art and discipline, as well college preparation courses. It aims to provide graduates with the best foundation for their future. Admission is based on audition and interview. Admission does not require academic credit, but students who excel as artists should be motivated.
Scholarships
Preparatory schools have many scholarship options. While most schools have their financial aid offices, some schools also offer external scholarships. Many schools offer athletic and merit scholarships. These scholarships may be eligible for an application. Others require a specific GPA and/or athletic achievement.
Scholarships are available to students in their senior or junior years of high school. For these awards to be eligible, you must have a minimum GPA (3.0). They can pay up to $90,000. Many schools require applicants to submit their applications by a particular date. However, some schools might be more flexible.
Independent learning environment
Independent schools offer students an opportunity to receive a more personalized, multidisciplinary education. Teachers can design their curriculum according to student learning styles, needs, and interests. In addition, they can use their preferred methods of assessing student achievement. Faculty members are also eligible for professional development. Faculty members also have the opportunity to receive professional development opportunities. Small classes and low student-teacher ratios encourage close relationships between students and instructors. Students have many opportunities to learn and grow outside the classroom.
Teachers can model and encourage independent learning in a variety of ways. Teachers can give feedback to students on their work, helping them to improve their confidence and spot mistakes. In order to support their learning, students can receive after-school study assistance. After-school learning activities allow students to demonstrate their willingness and ability to take control of learning goals and motivate themselves.
FAQ
How long should I spend studying each semester
The time you spend studying will depend on several factors.
In addition to these factors, some schools may require you to take certain classes yearly. This means that you won't always be able take the same courses every semester. You can ask your advisor to tell you which courses you need to take each semester.
What is the difference between college or school?
Schools are usually divided into classes (or grades), with a teacher who is responsible for teaching a specific class. Colleges are larger organizations that offer more specialized programs and often include university-level courses. Colleges may focus more on business and science while schools will usually only teach basic subjects. The curriculum at both levels is intended to prepare students to study at higher levels.
Should I specialize in one subject or branch out?
Many students choose to concentrate on one subject (e.g. English History and Math) rather that branching into several subjects. But, you don't always have to specialize. You could, for example, choose to specialize in surgery or internal medicine if you are considering becoming a physician. You could also choose to specialize in family practice, pediatrics, gerontology or neurology. If you're interested in a career as a business professional, you can focus on management, finance or operations research. The decision is up to you.
How do I select my major?
Students choose their majors based upon their interests. Students may choose to major in the subject they are most passionate about because it is easier than learning something else. Others are interested in a career where there are few jobs. Others choose a major to make money while they study. Whatever your reasons, you should consider what kind of job you might like after graduation.
There are many options for information on different areas of study. Talk to your family and friends about their experiences. Read magazines and newspapers to see if there are any careers listed. Talk to your guidance counselor at school to learn more about possible careers. Visit Career Services in your local library. Check out books related to various topics at your library. You can search the Internet for information about specific careers.
What are the different types of early childhood education?
There are many ways that early childhood education can be described. These are the most popular:
-
Preschool - Children ages 2 to 5
-
PreKindergarten – Children aged 4-6
-
Head Start/Headstart - Children from 0-3 Years
-
Day Care/ Daycares: Children 0-5
-
Child Care Centers: Children from 0-18
-
Family Child Care for Children Ages 0-12
-
Home schooling - Children aged KG to 16.
Statistics
- Globally, in 2008, around 89% of children aged six to twelve were enrolled in primary education, and this proportion was rising. (en.wikipedia.org)
- And, within ten years of graduation, 44.1 percent of 1993 humanities graduates had written to public officials, compared to 30.1 percent of STEM majors. (bostonreview.net)
- “Children of homeowners are 116% more likely to graduate from college than children of renters of the same age, race, and income. (habitatbroward.org)
- Data from the Department of Education reveal that, among 2008 college graduates, 92.8 percent of humanities majors have voted at least once since finishing school. (bostonreview.net)
- They are more likely to graduate high school (25%) and finish college (116%). (habitatbroward.org)
External Links
How To
How do I enroll in homeschooling?
Homeschooling means that children are educated at home using a variety methods like reading books, watching videos or doing exercises. It is considered one of the most effective ways of learning because it enables students to learn things at their own pace and develop skills like problem-solving, critical thinking, creativity, self-discipline, communication, and social skills.
People who wish to educate their children at their home are more common than ever, particularly parents who work full-time but don't have enough time for their children. If this is the case, they have two options: homeschooling or a private school. This allows them to spend their time and energy on education instead of worrying about whether someone will be available to look after their children.
Homeschooling has many benefits. They can develop their ability to think critically and create, increase their knowledge, improve their language skills, develop their identity, become independent learners and have greater control over their lives than if they were in school.
Homeschooling has one main goal: to give quality education to children in order to help them become successful adults. Before you can start homeschooling, there are some things that you need to do. You must determine if your child is eligible for public or private school. The type of curriculum that you choose to use for homeschooling is an important consideration. There are many curricula that you can find online, depending on your budget and expertise. Some of these include classical, Montessori, Waldorf, Reggio Emilia, Charlotte Mason, unschooling, natural learning, and others. You must also ensure that you have all the resources necessary to educate your child before you start homeschooling. This involves purchasing books, educational material, computers, digital devices, toys, games and musical instruments. You can buy these items online or purchase them from local stores.
Once you've completed the above steps successfully, you can register yourself as a parent who homeschools. To do this, contact your state department or education for assistance. They will help with the forms and give you advice on how you can start homeschooling.